- Отправить по электронной почте : David@tmaxcn.com
- Отправить по электронной почте : Davidtmaxcn@gmail.com
- : No. 39, Xinchang Road, Xinyang, Haicang Dist., Xiamen, Fujian, China (Mainland)
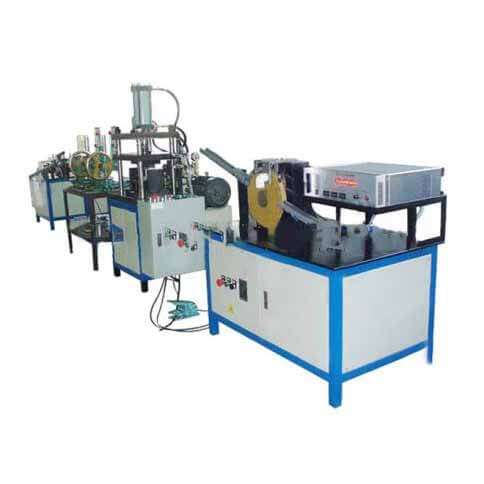
Supercapacitors, also known as ultracapacitors or electrochemical capacitors, are energy storage devices that offer high power density, rapid charge/discharge cycles, and long cycle life compared to conventional batteries. Setting up a supercapacitor production line involves multiple stages and a variety of specialized equipment. Here's an overview of the process and key components:
1. Raw Material Preparation
Activated Carbon
Production: High surface area activated carbon is crucial for supercapacitors. It is typically produced from coconut shells, coal, or other carbon-rich materials through pyrolysis and activation.
Quality Control: Ensuring uniform particle size and surface area for optimal performance.
Electrolytes
Types: Commonly used electrolytes include aqueous solutions (e.g., sulfuric acid, potassium hydroxide) and organic solutions (e.g., acetonitrile, propylene carbonate).
Purity: High purity is essential to avoid impurities that can degrade the performance.
Binders and Conductive Additives
Polymers: Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF), etc.
Conductive Carbon: Carbon black, graphite, etc.
Mixing and Coating
Mixers: High-shear mixers or planetary mixers are used to combine activated carbon with binders and conductive additives.
Coating Machines: Coating the slurry onto current collectors (aluminum or copper foils) using techniques such as doctor blade, slot-die coating, or screen printing.
Drying Ovens: Removing solvents to leave a solid electrode material.
Calendering
Roll Presses: Compressing the electrode material to achieve desired thickness and density.
Electrode Cutting and Stacking
Laser or Die Cutting: Precise cutting of electrodes to the required size.
Battery Stacking Machine: Aligning and stacking electrodes and separators.
Electrolyte Filling
Vacuum Filling Machines: Ensuring the electrolyte fully impregnates the electrode material without air bubbles.
Packaging
Pouch Cells: Sealing electrodes and electrolyte in laminated aluminum pouches.
Can Cells: Encasing in metal or plastic cylindrical or prismatic cans.
Sealing
Heat Sealing: For pouch cells.
Welding: Laser or ultrasonic welding for can cells.
Initial Charging
Formation Process: Gradual charging of the cell to form the electric double layer and activate the electrodes.
Cycling: Repeated charging and discharging to stabilize performance.
Testing
Electrical Testing: Capacitance, internal resistance, leakage current, and cycle life testing.
Environmental Testing: Performance under different temperatures and humidity levels.
Inspection
Visual Inspection: Checking for physical defects.
X-ray Inspection: Ensuring proper assembly and electrolyte distribution.
Final Packaging
Labeling and Barcoding: For traceability.
Packing: Proper packaging to protect during shipping.
Key Equipment in a Supercapacitor Production Line
Raw Material Processing Equipment:
Pulverizers, Mixers, Dryers
Electrode Manufacturing Equipment:
Coaters, Drying Ovens, Calendering Machines
Cell Assembly Equipment:
Cutting Machines, Stacking Machines, Electrolyte Filling Machines
Sealing Equipment:
Heat Sealers, Welding Machines
Formation and Testing Equipment:
Formation Chargers, Test Stations
Quality Control Equipment:
Inspection Systems (visual, X-ray)
Setting up a supercapacitor production line involves significant investment in equipment, research and development, and strict quality control processes to ensure the production of high-performance, reliable supercapacitors.
 ru
ru English
English










 +86 13174506016
+86 13174506016 David@tmaxcn.com
David@tmaxcn.com

